Photo by Patrick Fore on Unsplash
Linux Introduction and Installation
Linux philosophy:'laugh in the face of danger'
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
📄This article will help the reader navigate the world of Linux by introducing the concepts like Linux kernel, distributions, and the difference between the various flavors of linux.
Ubuntu and CentOS remain the most used linux distributions. However, Debian and Fedora saw their user base explode at an exponential rate in 2022. The popularity and the applications of different flavors of linux can be understood with the help of infographics depicted below:
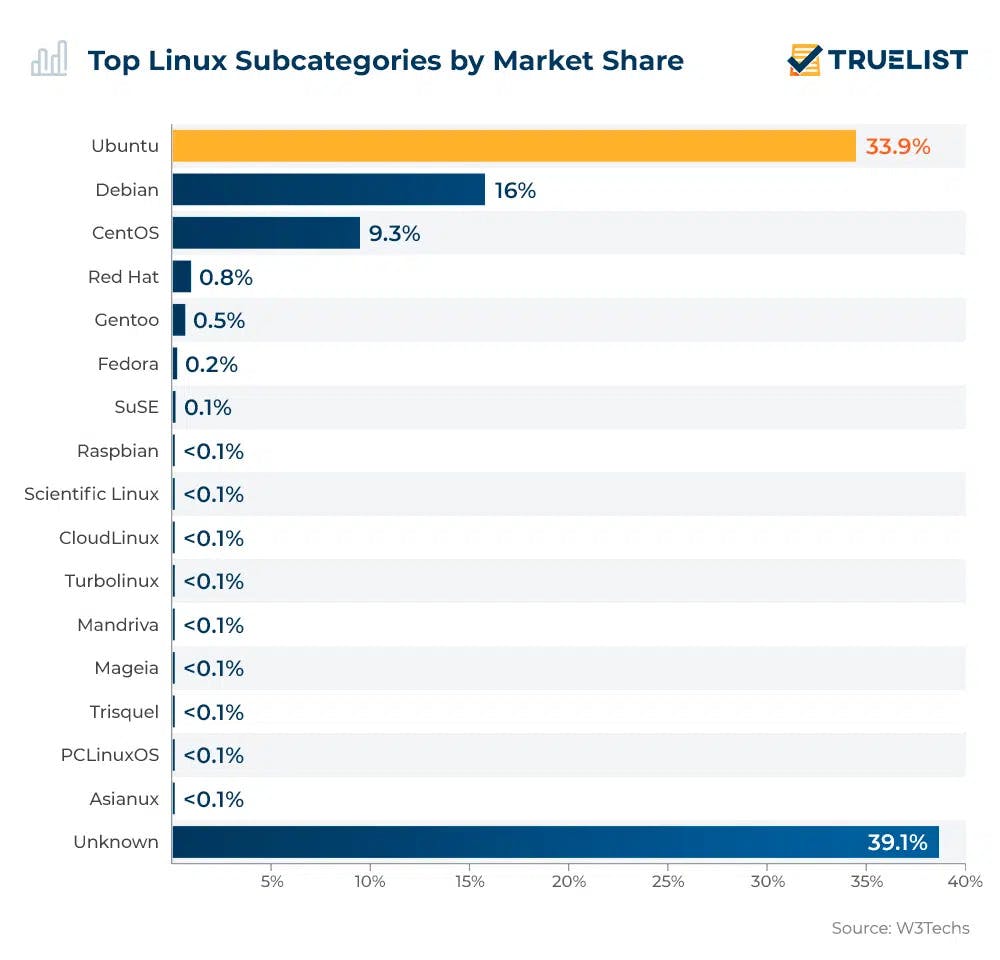
Now, you might wonder- what are these flavors? and what is a kernel? As I am on a diet, I wouldn't be able to provide you with flavors of ice cream. However, I can provide you with ample data illustrating the various ways the linux kernel has been modified to suit the needs of the users and serve distinct categories of individuals efficiently. Whether it be hacking, an alternative to other operating systems like Windows, sophisticated CLI tools, email and data servers, or any other type of shared servers, we can use the linux kernel with modifications to satisfy our requirements or use any publicly available distributions to eventually achieve our purpose. Several popular families and flavors of linux are listed below:
1- Debian 2- Fedora 3- CentOS 4- Kali Linux 5- Ubuntu
Distributions of linux are often referred to as distros as well. The mission of Ubuntu Linux can be best understood by the African philosophy of "being self through others". The operating systems can be classified into 2 types/categories:
1- Desktop Based 2- Server Based
Several examples of Desktop based operating systems are Windows, Mac OS, and Ubuntu Linux. When we talk about server-based operating systems, we are talking about RHEL(Redhat Enterprise Linux), CentOS, and several other operating systems designed to facilitate the users' needs.
The kernel is a system program that interacts with the hardware of the system. It provides a bridge between the software and hardware and serves as the most essential part of the computer. Some developers often confuse firmware with kernel but it is essential to know that both play different roles in a system. A kernel is software that serves as an interface between the application and the hardware. Firmware, on the other hand, runs on the hardware itself.
When we compare Windows with Linux, we realize that Linux is open source while the former is owned by Microsoft and thus a proprietary software. While comparing both operating systems on a technical level, we realize that Windows uses ACL while Linux uses POSIX ACL. Linux is considered more secure and customizable as compared to Windows OS because of its intrinsic nature of file permissions and open-source availability. Windows uses an NTFS file system while Linux applies the ext file system. NTFS is an acronym for New Technology File System while the ext stands for the extendable file system. An ext file system provides great support for large file sizes and drivers but when compared to the NTFS file system, its file handling capabilities do come in short. The NTFS file system was introduced as a proprietary journaling file system,
Let's go forward with the installation of Ubuntu Linux on a mainframe utilizing Windows OS.
We will use VirtualBox for the same and create a virtual machine to run the Ubuntu Linux. Another way to run Linux on your computer with a different operating system already present on the computer is to efficiently use the method of dual booting. Let us explore the brief simplification of the dual booting process initially while the virtual machines wait for us at the end of the article informing us about how to save computational resources.
The requirements for dual booting are as follows: 1- A USB drive with at least 4 GB storage. You would have to remove all the data from the pen drive and store it in a safe place in your system or any other backup device. 2- A computer with a partitioned hard drive and internet connection. 3- BIOS in UEFI(Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). 4- Ubuntu ISO image(Linux distro) and Rufus(bootable USB creation tool).
UEFI(Unified Extensible Firmware Instruction) and Legacy systems are the two types of BIOS currently available in computer systems. UEFI allows for the processing of larger files and large driver sizes. Legacy systems have limitations as they cannot handle large driver sizes which exceed 2.1 TB and only have text-only menus in their setup programs. UEFI also comes with beautiful graphics while booting the computer. You can partition your hard drive in the disk management utility provided by Windows.
How to partition the hard drive in your disk management:
Step 1: Type in windows key->Type 'Disk Management. Click the contextual option.
Step 2: Right-click the unallocated region/space in disk management, and assign a new letter after creating it as a new volume.
Step 3: Format the partition and you are good to go.
Step 4: Finalize your choices and complete the process.
ubuntu.com/download/desktop: visit this site to get the iso files of linux and download them to your local PC.
You are supposed to mount the distro in the USB and then configure the OS as a part of your system by accessing the BIOS settings when the computer starts. The process dictates that you boot the OS from the drive and run the installation wizard.
How to mount the distro in the USB[using rufus]: Step 1: Download Rufus. Open the Rufus application. Step 2: Keep the partition scheme as MBR and the target system as BIOS or UEFI. Step 3: Keep the default values for all the other fields and proceed with the installation. Step 4: Complete the writing process and close the installation wizard.
This will write the OS to your USB drive. Make sure to write the appropriate ISO file and decide upon the accurate USB drive selection.
After the above process is completed, restart the computer.
While the booting process is being initiated, press the F12 key which allows accessing the boot menu. Do make note that you should press the key before the booting process is completed. The bootable USB drive will show up in the boot menu. Select the USB drive and then follow the installation procedure as illustrated in the installation wizard.
I will guide you through the installation wizard as it is identical to the process that we are going to use in the installation of the virtual machine in the VirtualBox.
How to install Ubuntu Linux as a virtual machine in the VirtualBox:
Step 1-> Installation and configuration of Virtualbox 🎯Go to the site: virtualbox.org 🎯Download the software and run the installation wizard on your computer.
Step 2-> Installation and configuration of Ubuntu 🎯Select the appropriate start-up optical disk for the virtual machine after creating a new instance for the same. 🎯Follow the wizard with appropriate directions. 🎯Some of the images for your reference: